The Glutamatergic Synapse
Par un écrivain mystérieux
Last updated 10 juillet 2024
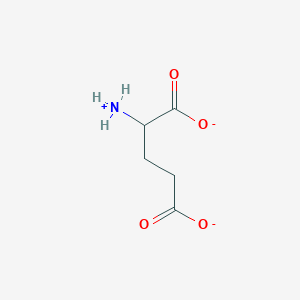
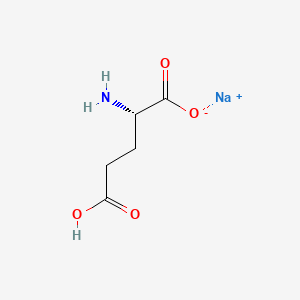
In the mammalian central nervous system (CNS), glutamate is the predominant excitatory neurotransmitter. It is estimated that more than half of all synapses release glutamate and that almost all excitatory neurons in the CNS are glutamatergic.

Kainate receptor modulation of glutamatergic synaptic transmission in the CA2 region of the hippocampus - Falcón‐Moya - 2021 - Journal of Neurochemistry - Wiley Online Library

Group 1 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors in Neurological and Psychiatric Diseases: Mechanisms and Prospective - Li-Da Su, Na Wang, Junhai Han, Ying Shen, 2022

Figure 1, Schematic drawing of a glutamatergic synapse, with postsynaptic AMPA, NMDA, KA and metabotropic receptors - Jasper's Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies - NCBI Bookshelf
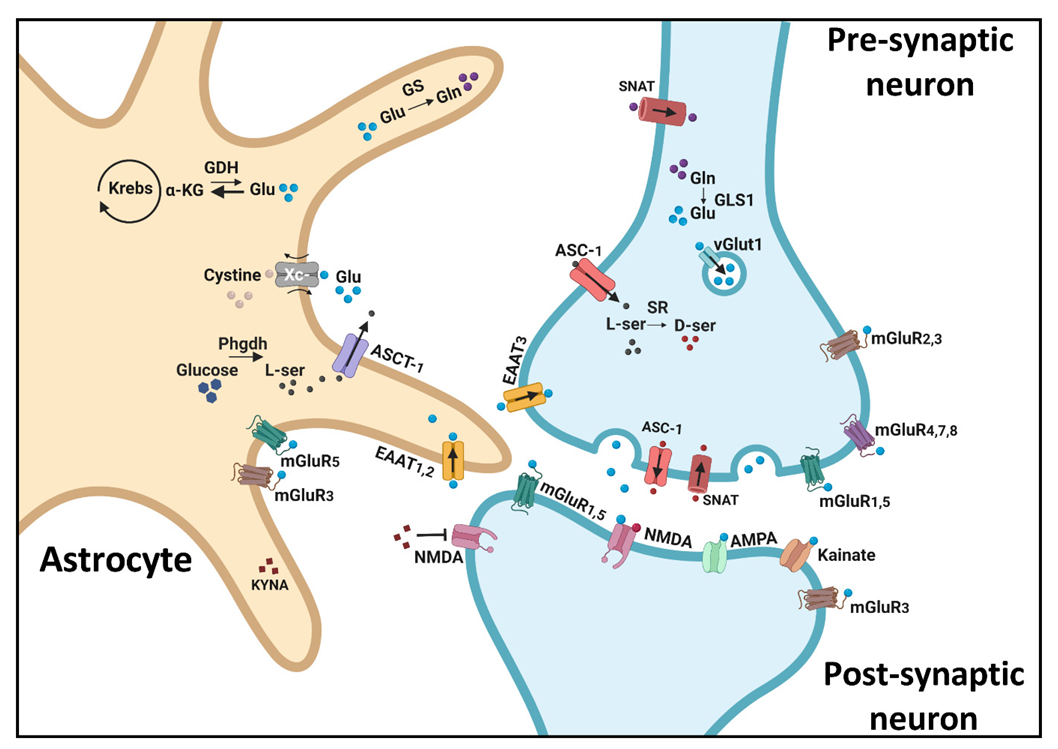
IJMS, Free Full-Text
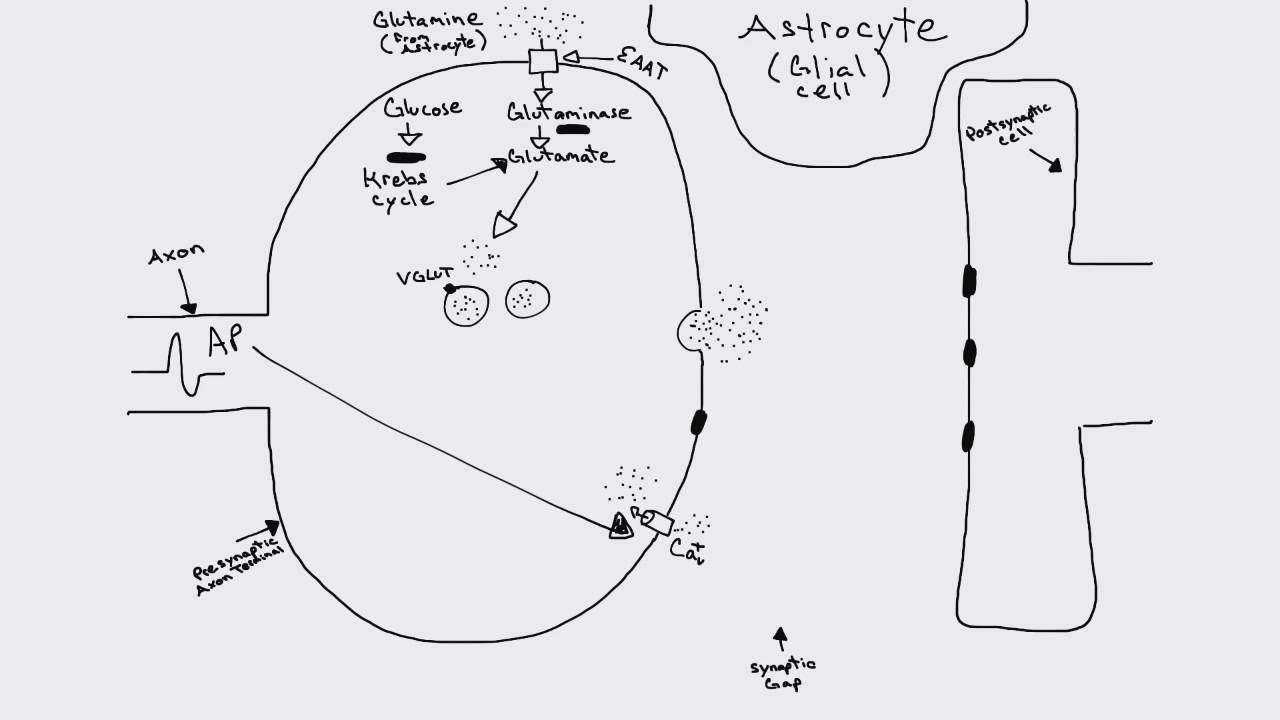
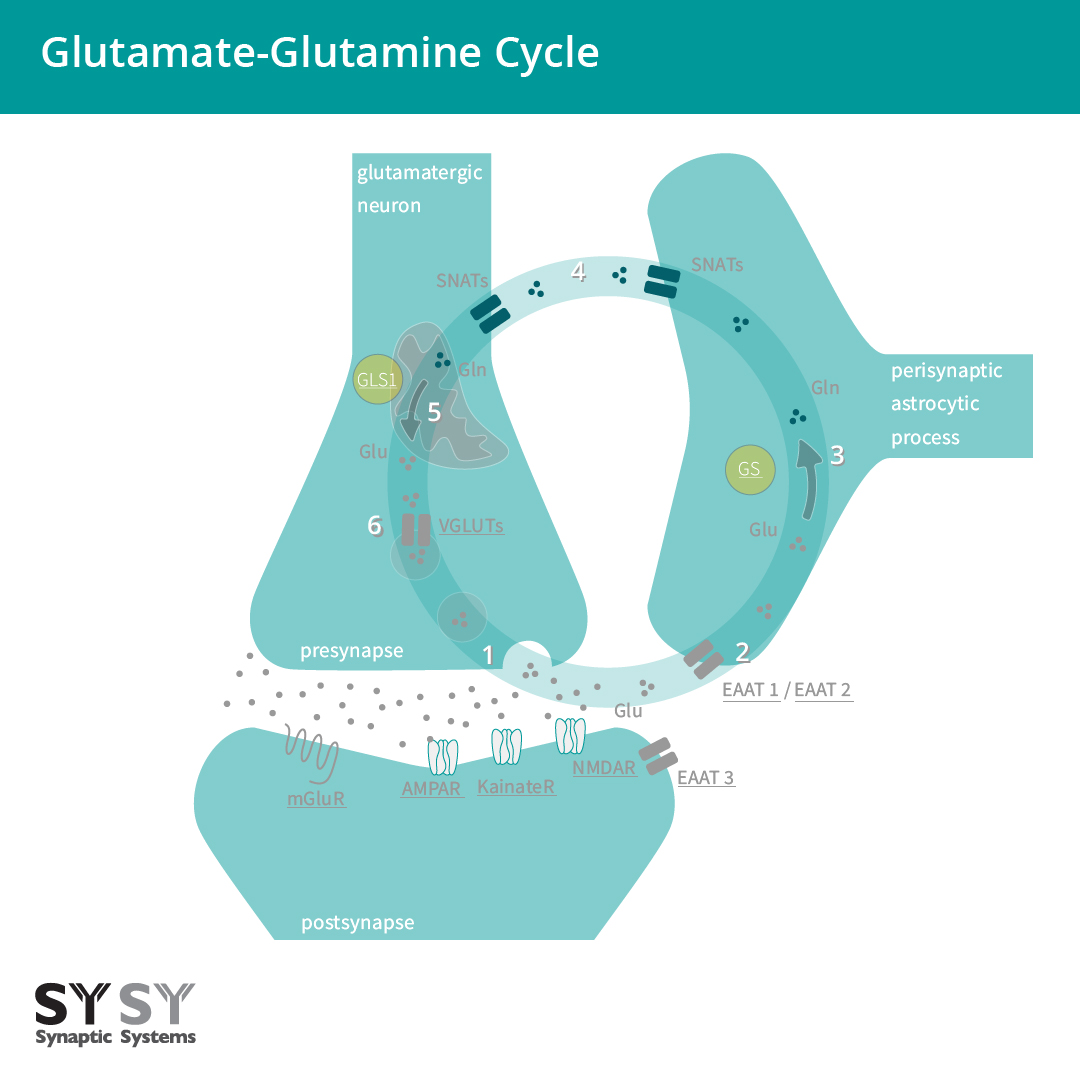
Glutamatergic Synapse
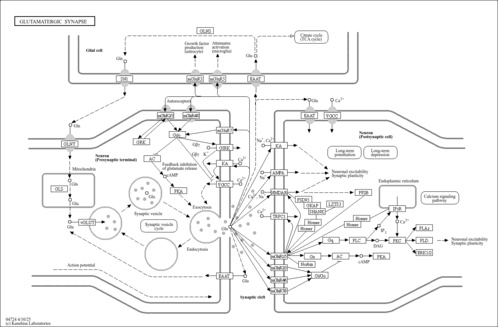
KEGG PATHWAY: hsa04724

Unique transsynaptic complexes enable long-term synaptic plasticity in a synapse-specific manner
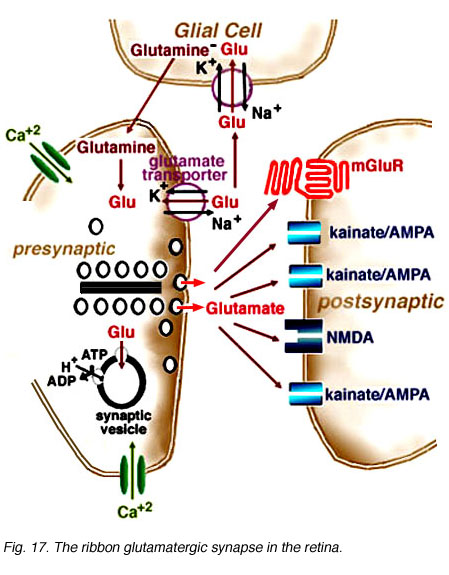
Glutamate and glutamate receptors in the vertebrate retina by Victoria Connaughton – Webvision

Neurotransmitters: Glutamate, What do glutamate neurotransmitters do?

GABA fluctuations driven by astrocytic Glu/ GABA exchange explain synaptic acuity

Tomas Malinauskas on X: Activating (glutamatergic) and inhibitory (GABAergic) synapses play key roles in regulating brain function. Glutamatergic synapses use glutamate, the the brain's excitatory neurotransmitter. 1/n / X

The role of transporters and synaptic cleft morphology in glutamate and GABA homeostasis and their effect on neuronal function
Recommandé pour vous
 Le glutamate monosodique (E621) - Vidya-Shop14 Jul 2023
Le glutamate monosodique (E621) - Vidya-Shop14 Jul 2023 GLUTAMATE MONOSODIQUE E 622 SAC DE 25 KG14 Jul 2023
GLUTAMATE MONOSODIQUE E 622 SAC DE 25 KG14 Jul 2023 Glutamate - Paris Store14 Jul 2023
Glutamate - Paris Store14 Jul 2023- Glutamate, C5H8NO414 Jul 2023
- Glutamate - PsychonautWiki14 Jul 2023
 Sodium lauroyl glutamate, CAS 29923-31-714 Jul 2023
Sodium lauroyl glutamate, CAS 29923-31-714 Jul 2023 Glutamate monosodique, description et recettes sur Lucullent!14 Jul 2023
Glutamate monosodique, description et recettes sur Lucullent!14 Jul 2023 GoodTherapy14 Jul 2023
GoodTherapy14 Jul 2023 Difference Between Glutamine and Glutamate Compare the Difference Between Similar Terms14 Jul 2023
Difference Between Glutamine and Glutamate Compare the Difference Between Similar Terms14 Jul 2023- Monosodium Glutamate, C5H8NNaO414 Jul 2023
Tu pourrais aussi aimer
 Rainbow High Blue Doll - Kim Nguyen – L.O.L. Surprise14 Jul 2023
Rainbow High Blue Doll - Kim Nguyen – L.O.L. Surprise14 Jul 2023 Couvercle De Plafond Conduit De Ventilation Filet Anti-insectes Diamètre 100 mm14 Jul 2023
Couvercle De Plafond Conduit De Ventilation Filet Anti-insectes Diamètre 100 mm14 Jul 2023 Basket-ball Sport Tapis en Peluche Living Room Tapis de Chambre à Coucher Décoration d'intérieur Marron Basketball Starry Blue Enfants Garçon Chambre14 Jul 2023
Basket-ball Sport Tapis en Peluche Living Room Tapis de Chambre à Coucher Décoration d'intérieur Marron Basketball Starry Blue Enfants Garçon Chambre14 Jul 2023 Jouets de caméra pour enfants pour les garçons de 3 à 9 ans filles14 Jul 2023
Jouets de caméra pour enfants pour les garçons de 3 à 9 ans filles14 Jul 2023 Balance De Cuillère, Balance De Cuillère Numérique 500g/0.1g, Balance De Cuillère Numérique Pour Cuillère Simple De Restaurant à La Maison14 Jul 2023
Balance De Cuillère, Balance De Cuillère Numérique 500g/0.1g, Balance De Cuillère Numérique Pour Cuillère Simple De Restaurant à La Maison14 Jul 2023 Vichona Nouveau Cadeau De Bébé,Double-faced Décision Coin comme Nouveaux Parents Cadeaux pour Couples,Dovely Bébé Douche Cadeaux comme Nouvelle14 Jul 2023
Vichona Nouveau Cadeau De Bébé,Double-faced Décision Coin comme Nouveaux Parents Cadeaux pour Couples,Dovely Bébé Douche Cadeaux comme Nouvelle14 Jul 2023 Distributeur de boissons froides 4 x 12 L - DELUXE12/414 Jul 2023
Distributeur de boissons froides 4 x 12 L - DELUXE12/414 Jul 2023 How to Set Up Your Philips Hue Bridge14 Jul 2023
How to Set Up Your Philips Hue Bridge14 Jul 2023 PerfectDraft's Beer Machine Is The Ultimate Last-Minute Gift For14 Jul 2023
PerfectDraft's Beer Machine Is The Ultimate Last-Minute Gift For14 Jul 2023 Heidelberg Wallbox Home Eco 11 kW (Starting from €503.3614 Jul 2023
Heidelberg Wallbox Home Eco 11 kW (Starting from €503.3614 Jul 2023