IJMS, Free Full-Text
Par un écrivain mystérieux
Last updated 10 juillet 2024
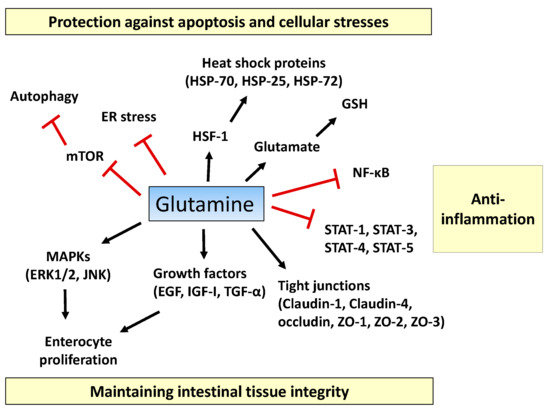
Glutamine, the most abundant free amino acid in the human body, is a major substrate utilized by intestinal cells. The roles of glutamine in intestinal physiology and management of multiple intestinal diseases have been reported. In gut physiology, glutamine promotes enterocyte proliferation, regulates tight junction proteins, suppresses pro-inflammatory signaling pathways, and protects cells against apoptosis and cellular stresses during normal and pathologic conditions. As glutamine stores are depleted during severe metabolic stress including trauma, sepsis, and inflammatory bowel diseases, glutamine supplementation has been examined in patients to improve their clinical outcomes. In this review, we discuss the physiological roles of glutamine for intestinal health and its underlying mechanisms. In addition, we discuss the current evidence for the efficacy of glutamine supplementation in intestinal diseases.

Readwise YAML formating - Help - Obsidian Forum
IJMS, Free Full-Text, test vivo
International Journal of Molecular Medicine
IJMS, Free Full-Text, synapse x twitter

Value LeaderIJMS, Free Full-Text, your channel
IJMS, Free Full-Text, synapse x twitter
IJMS, Free Full-Text, test vivo
IJMS, Free Full-Text, test vivo
IJMS, Free Full-Text, bronstein meier ii
Recommandé pour vous
 NOW Supplements, L-Glutamine 500 mg, Nitrogen Transporter* Amino Acid, 120 Veg Capsules14 Jul 2023
NOW Supplements, L-Glutamine 500 mg, Nitrogen Transporter* Amino Acid, 120 Veg Capsules14 Jul 2023 Optimum Nutrition - Glutamine Powder - Recovery and immunity - TRU·FIT14 Jul 2023
Optimum Nutrition - Glutamine Powder - Recovery and immunity - TRU·FIT14 Jul 2023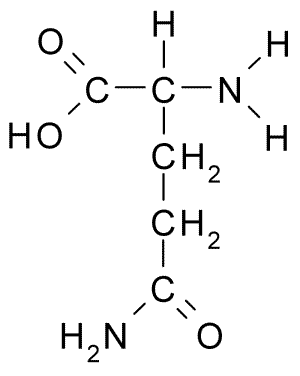 File:L-Glutamine.png - Wikipedia14 Jul 2023
File:L-Glutamine.png - Wikipedia14 Jul 2023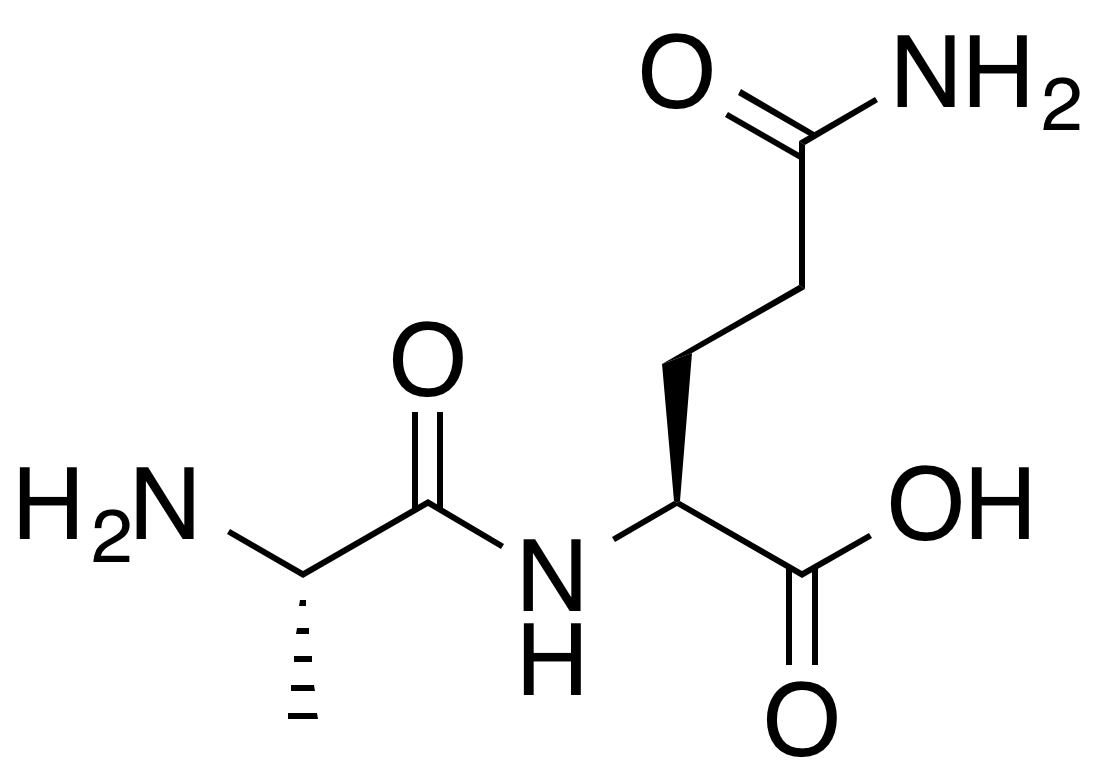 Alanyl-glutamine - Wikipedia14 Jul 2023
Alanyl-glutamine - Wikipedia14 Jul 2023 R1 Glutamine14 Jul 2023
R1 Glutamine14 Jul 2023 Glutamine14 Jul 2023
Glutamine14 Jul 2023 GLUTAMINE MICRONIZED, Glutamine Micronized, Amino Acids, Products14 Jul 2023
GLUTAMINE MICRONIZED, Glutamine Micronized, Amino Acids, Products14 Jul 2023 L-Glutamine 1000mg, 100 gélules Boticinal Laboratoire - Parapharmacie Boticinal14 Jul 2023
L-Glutamine 1000mg, 100 gélules Boticinal Laboratoire - Parapharmacie Boticinal14 Jul 2023 Radiance™ Amino Glutamine (L-Glutamine Powder)14 Jul 2023
Radiance™ Amino Glutamine (L-Glutamine Powder)14 Jul 2023 Glutamine Complex PLG-U Powder - Physica Energetics14 Jul 2023
Glutamine Complex PLG-U Powder - Physica Energetics14 Jul 2023
Tu pourrais aussi aimer
 Marque écologique d'accessoires fonctionnels et jolis pour maman14 Jul 2023
Marque écologique d'accessoires fonctionnels et jolis pour maman14 Jul 2023 On Tour 15 - Short de bain pour Homme14 Jul 2023
On Tour 15 - Short de bain pour Homme14 Jul 2023 Drap-housse 140x190 beige en coton ROZZO14 Jul 2023
Drap-housse 140x190 beige en coton ROZZO14 Jul 2023 Best CPU coolers in 202414 Jul 2023
Best CPU coolers in 202414 Jul 2023 Trousse Cactus Trousse À Crayons Anti-Salissant Trousse Scolaire Robuste Sac Porte-Stylo Pour Étudiants Scolaires Adulte : : Fournitures de bureau14 Jul 2023
Trousse Cactus Trousse À Crayons Anti-Salissant Trousse Scolaire Robuste Sac Porte-Stylo Pour Étudiants Scolaires Adulte : : Fournitures de bureau14 Jul 2023 Bouchons d'oreilles - Natation14 Jul 2023
Bouchons d'oreilles - Natation14 Jul 2023 Mangeoire ronde en acier Feeder Gardman14 Jul 2023
Mangeoire ronde en acier Feeder Gardman14 Jul 2023 Chargeur 24V 2A Plug GX12 - SMOLT AND CO14 Jul 2023
Chargeur 24V 2A Plug GX12 - SMOLT AND CO14 Jul 2023 Set Pyrex - Panier vapeur et son couvercle en verre (vir)14 Jul 2023
Set Pyrex - Panier vapeur et son couvercle en verre (vir)14 Jul 2023 Inserts de vis de réglage de chaleur en métal fileté en laiton M3-0.5 pour impression 3D, accessoires d'outils de fer à souder, M3 3mm, 50 pièces - AliExpress14 Jul 2023
Inserts de vis de réglage de chaleur en métal fileté en laiton M3-0.5 pour impression 3D, accessoires d'outils de fer à souder, M3 3mm, 50 pièces - AliExpress14 Jul 2023