Glutamate — Zebrafish UCL
Par un écrivain mystérieux
Last updated 27 juillet 2024
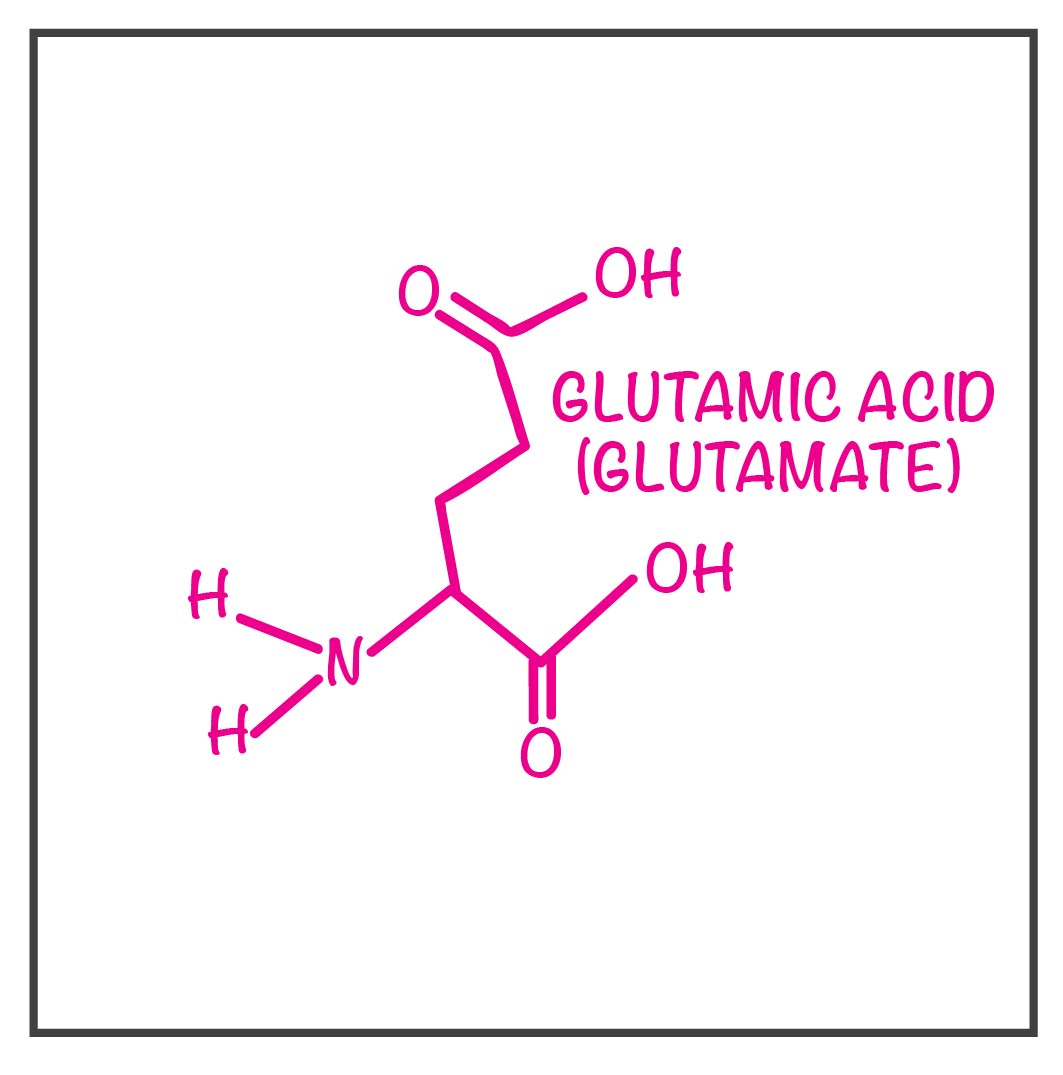
Glutamate is the anion of glutamic acid(an amino acid). It is the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the nervous system of the zebrafish and other vertebrates. Post-synaptic transmission of glutamate is mediated by four types of glutamate receptors: NMDA receptors : ionotropic transme

Neurotransmitters — Neurotransmitters — Zebrafish UCL

Polymersomes Eradicating Intracellular Bacteria
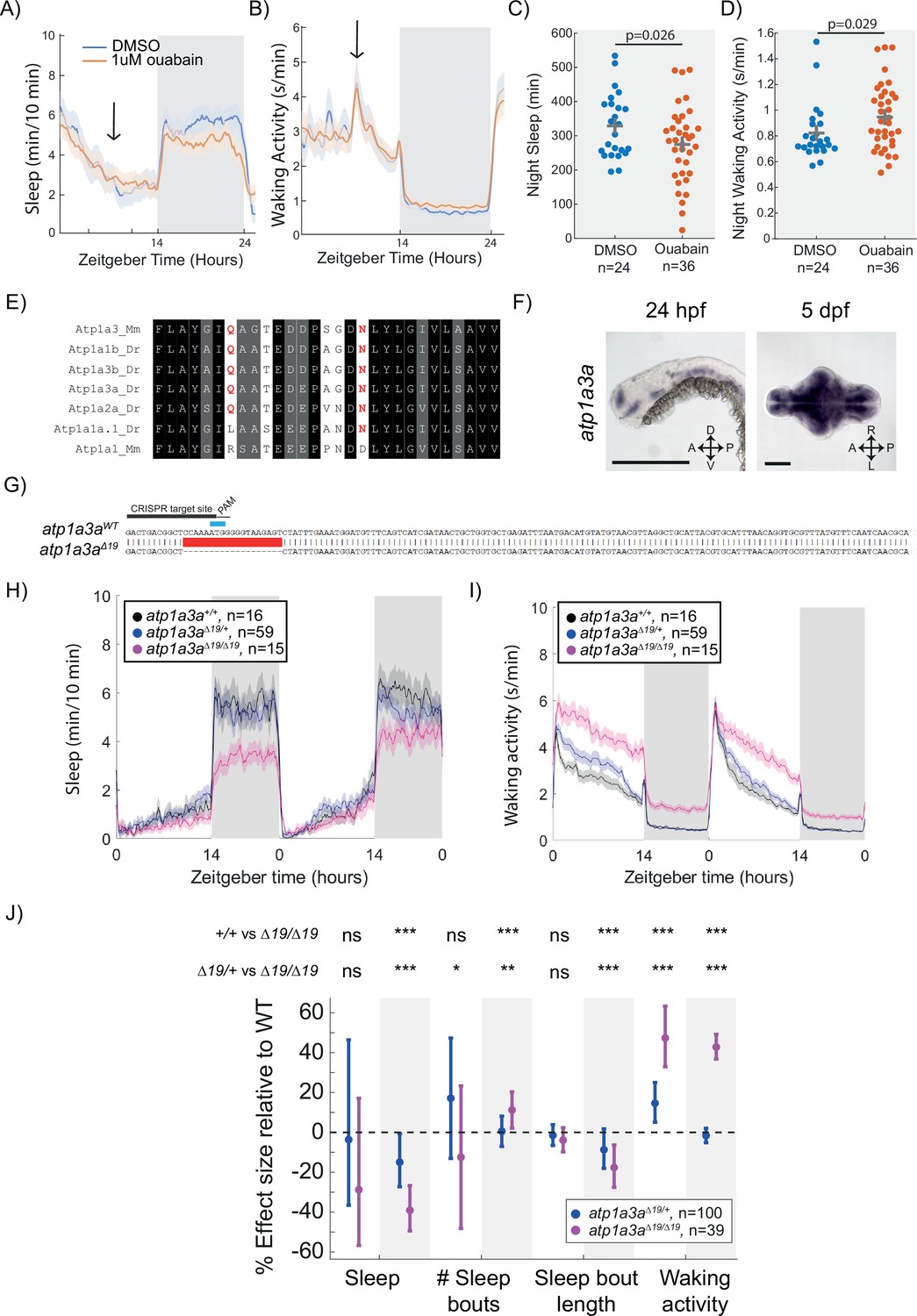
The zebrafish mutant dreammist implicates sodium homeostasis in

LTP Induction Boosts Glutamate Spillover by Driving Withdrawal of

Nitric Oxide Synthase Regulates Morphogenesis of Zebrafish Spinal

Analysis of human-zebrafish synteny adjacent to genes encoding
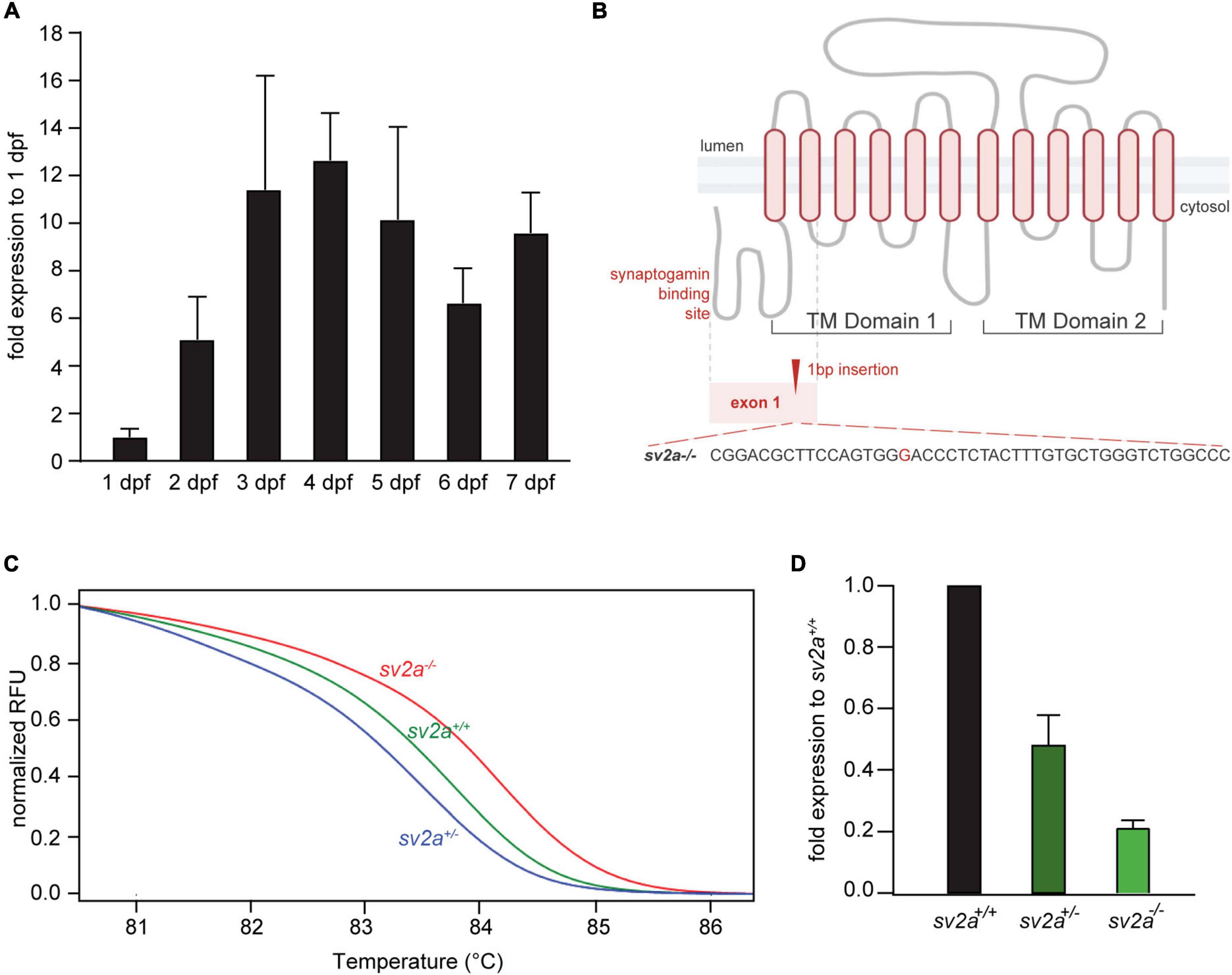
Frontiers Connectivity Mapping Using a Novel sv2a Loss-of
PDF) The Brilliance of the Zebrafish Model: Perception on Behavior

PDF] Miro dependent mitochondrial positioning is important for

The zebrafish mutant dreammist implicates sodium homeostasis in

Distinct phenotypes in zebrafish models of human startle disease

A review on the impacts of nanomaterials on neuromodulation and
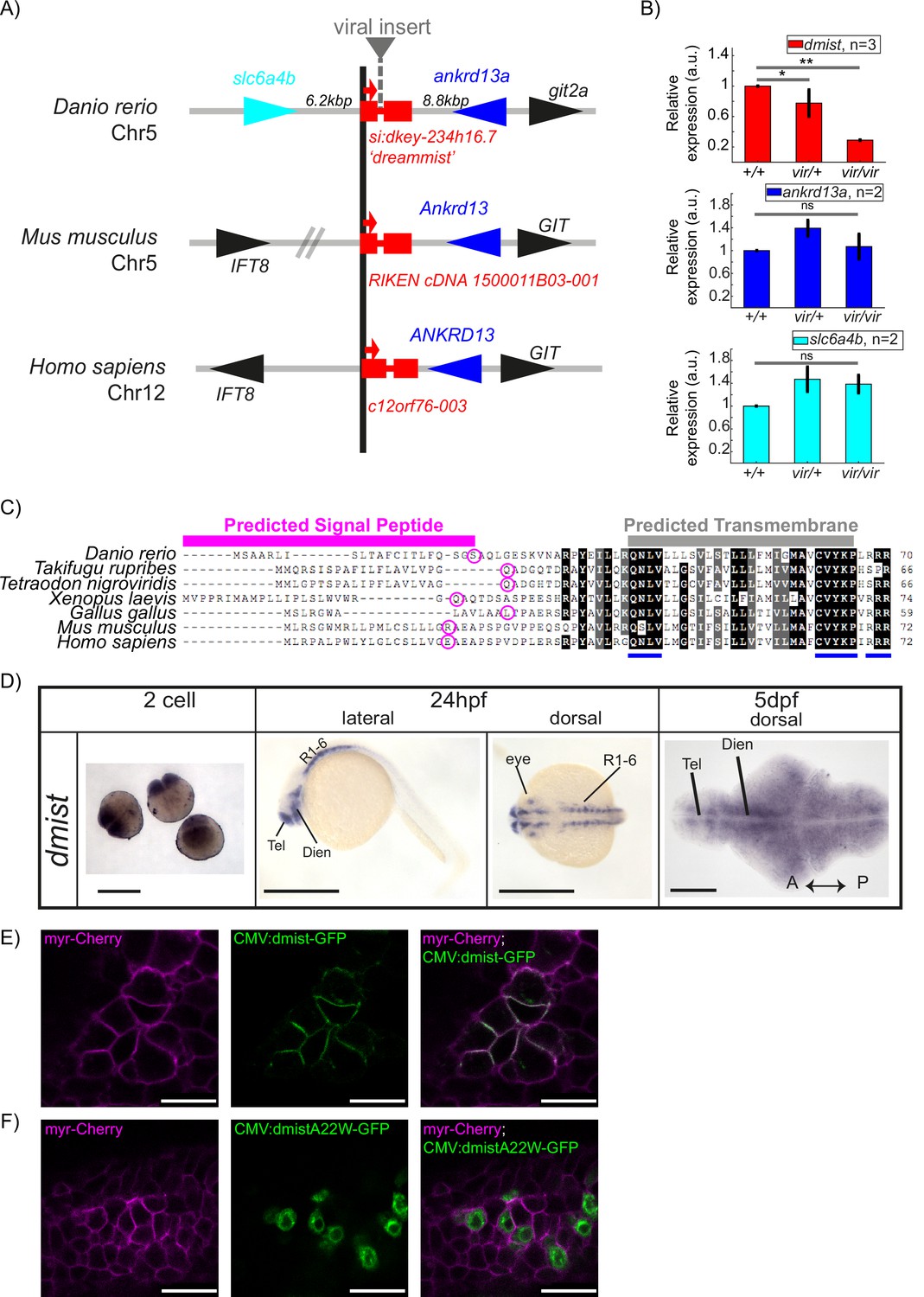
The zebrafish mutant dreammist implicates sodium homeostasis in
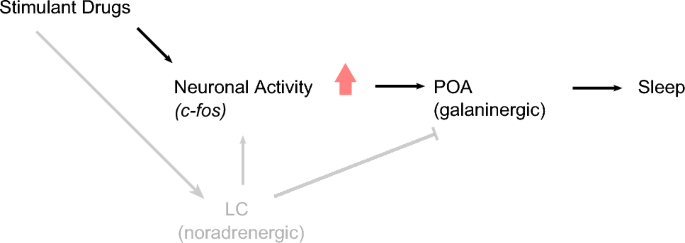
Noradrenergic tone is not required for neuronal activity-induced

Glutamate — Zebrafish UCL
Recommandé pour vous
 L'acide glutamique ou glutamate14 Jul 2023
L'acide glutamique ou glutamate14 Jul 2023 Bilingual neurons release glutamate and GABA14 Jul 2023
Bilingual neurons release glutamate and GABA14 Jul 2023 Sodium lauroyl glutamate, Surfactant14 Jul 2023
Sodium lauroyl glutamate, Surfactant14 Jul 2023 Glutamate - Paris Store14 Jul 2023
Glutamate - Paris Store14 Jul 2023 Glutamate monosodique, description et recettes sur Lucullent!14 Jul 2023
Glutamate monosodique, description et recettes sur Lucullent!14 Jul 2023 Glutamate - Bioblast14 Jul 2023
Glutamate - Bioblast14 Jul 2023 What is the Difference Between Glutamate and Glutamic Acid14 Jul 2023
What is the Difference Between Glutamate and Glutamic Acid14 Jul 2023 About Glutamate Toxicity – HOPES Huntington's Disease14 Jul 2023
About Glutamate Toxicity – HOPES Huntington's Disease14 Jul 2023 Ajinomoto monosodium glutamate 200gr14 Jul 2023
Ajinomoto monosodium glutamate 200gr14 Jul 2023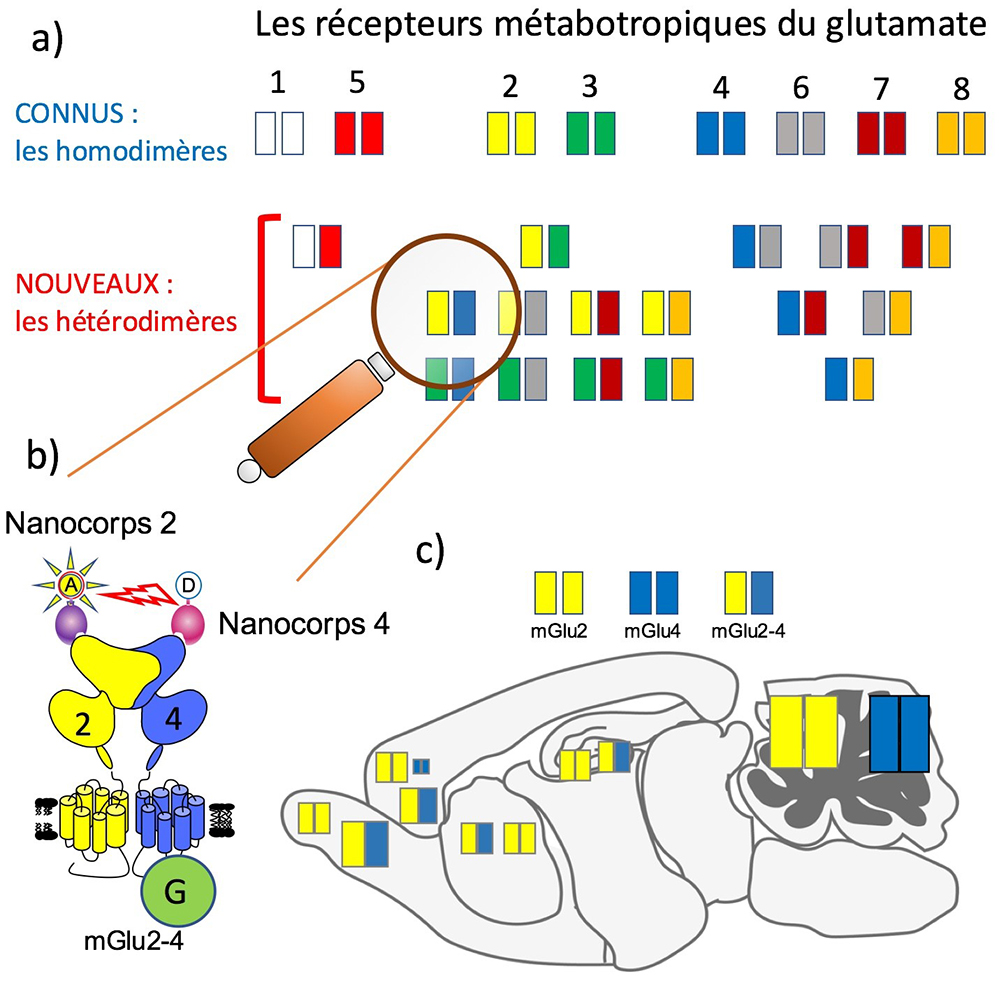 De nouveaux récepteurs du glutamate dans le cerveau14 Jul 2023
De nouveaux récepteurs du glutamate dans le cerveau14 Jul 2023
Tu pourrais aussi aimer
 Vidaxl - Coffret repousse piston de freins 40 pcs - - Coffrets outils - Rue du Commerce14 Jul 2023
Vidaxl - Coffret repousse piston de freins 40 pcs - - Coffrets outils - Rue du Commerce14 Jul 2023 Chargeur de voiture rapide double USB-A prix Tunisie - fiche14 Jul 2023
Chargeur de voiture rapide double USB-A prix Tunisie - fiche14 Jul 2023 de construction en bois en marbre pour cadeau d'anniversaire14 Jul 2023
de construction en bois en marbre pour cadeau d'anniversaire14 Jul 2023 Caribbean yacht charter fleet welcomes 67m superyacht CALEX to its ranks14 Jul 2023
Caribbean yacht charter fleet welcomes 67m superyacht CALEX to its ranks14 Jul 2023 USB USB Cables for sale14 Jul 2023
USB USB Cables for sale14 Jul 2023 Lot de 25 flacons en verre ambré 50ml avec pipette et bouchon rouge – O'dicy Cosmétiques14 Jul 2023
Lot de 25 flacons en verre ambré 50ml avec pipette et bouchon rouge – O'dicy Cosmétiques14 Jul 2023 Passe-Câble en plastique 60mm - Blanc14 Jul 2023
Passe-Câble en plastique 60mm - Blanc14 Jul 2023 Danone Danonino Strawberry Flavor Petit Suisse Cheese14 Jul 2023
Danone Danonino Strawberry Flavor Petit Suisse Cheese14 Jul 2023 Papier transparent - 70 x 100 cm, blanc14 Jul 2023
Papier transparent - 70 x 100 cm, blanc14 Jul 2023 Crème de tartre Great Value 100 g14 Jul 2023
Crème de tartre Great Value 100 g14 Jul 2023